Basic Anchor Positioning
The CSS anchor positioning module defines features that allow you to tether elements together. Elements can be defined as anchor elements and anchor-positioned elements. Anchor-positioned elements can be bound to anchor elements. The anchor-positioned elements can then have their size and position set relative to the size and location of the anchor elements to which they are bound.
– MDN Documents: Using CSS anchor positioning
Here for demonstration purpose, I have created a HTML document with a draggable area with a button that will trigger a popover menu. The popover menu will later be positioned relative to the button.
| |
(source code: 1-without-anchor-position.html)
Position Element Relative to Their Anchor
If you have done absolute position in the past you will know that by setting an element to be position:absolute and its parent to position:relative, the top/left/right/bottom of the element will be relative to the parent’s positioning.
Similarly, to associate the position of an element with an anchor, we first declare the anchor via anchor-name and position-anchor:
| |
Note that:
- in order for anchor-position to work, element has to be
position:fixedorposition:absolute - here we use
--in the anchor name to avoid collision with CSS native keywords (it may look alike a CSS variable, but it is NOT a variable !!!!) - an implicit anchor reference might be made (by default) between two element in some cases (e.g. the
<select>element and its drop-down picker)
Option-1: Position using anchor() function
CSS anchor positioning changes this paradigm, enabling anchor-positioned elements to be placed relative to the edges of their associated anchor(s). The module defines the
anchor()function, which is a valid value for each of the inset properties.When used, the function sets the inset position value (left/right/top/bottom/inset) as an absolute distance relative to the anchor element by defining the anchor element, the side of the anchor element the positioned element is being positioned relative to, and the distance from that side.
– MDN Document: Using inset properties with anchor () function values
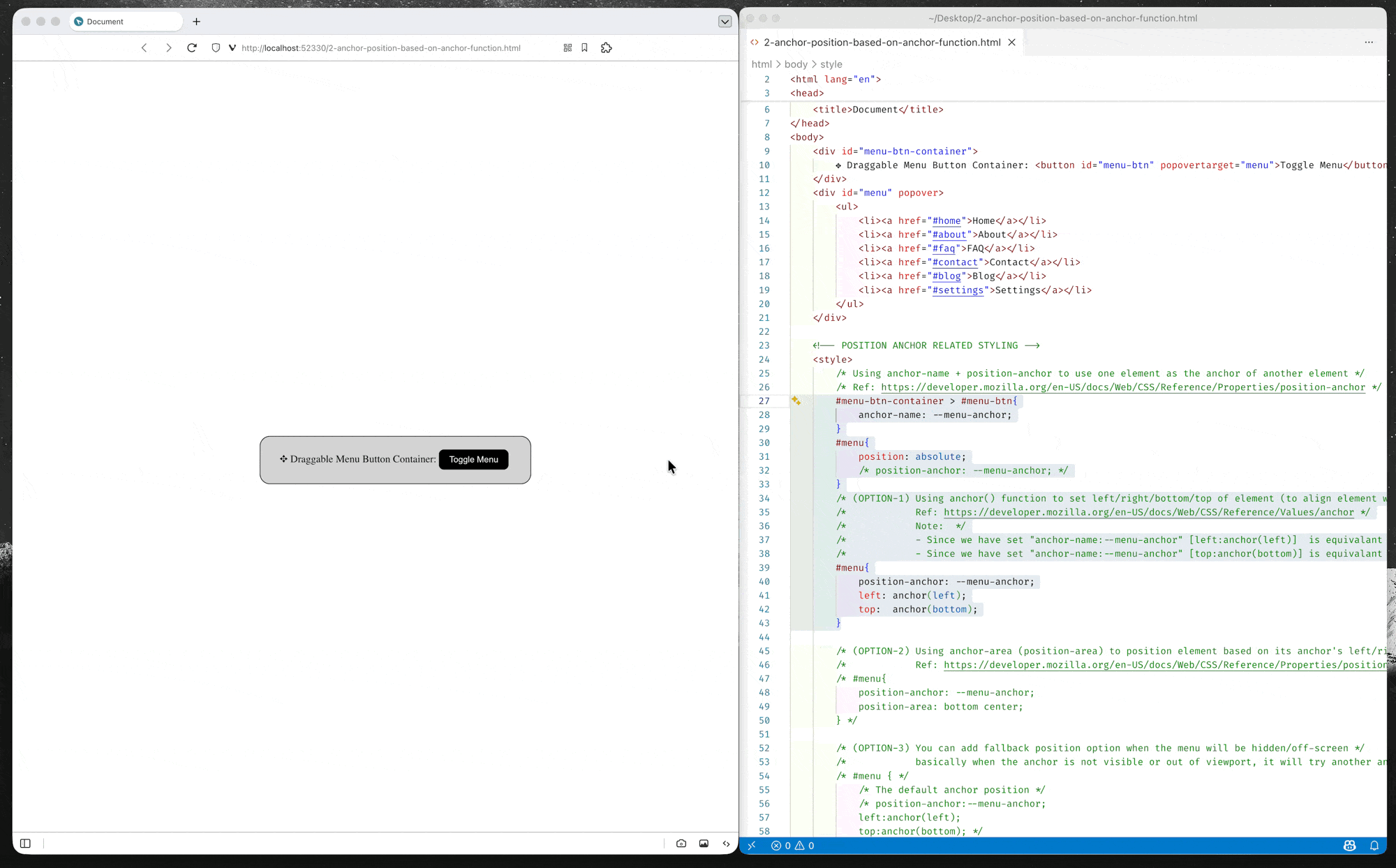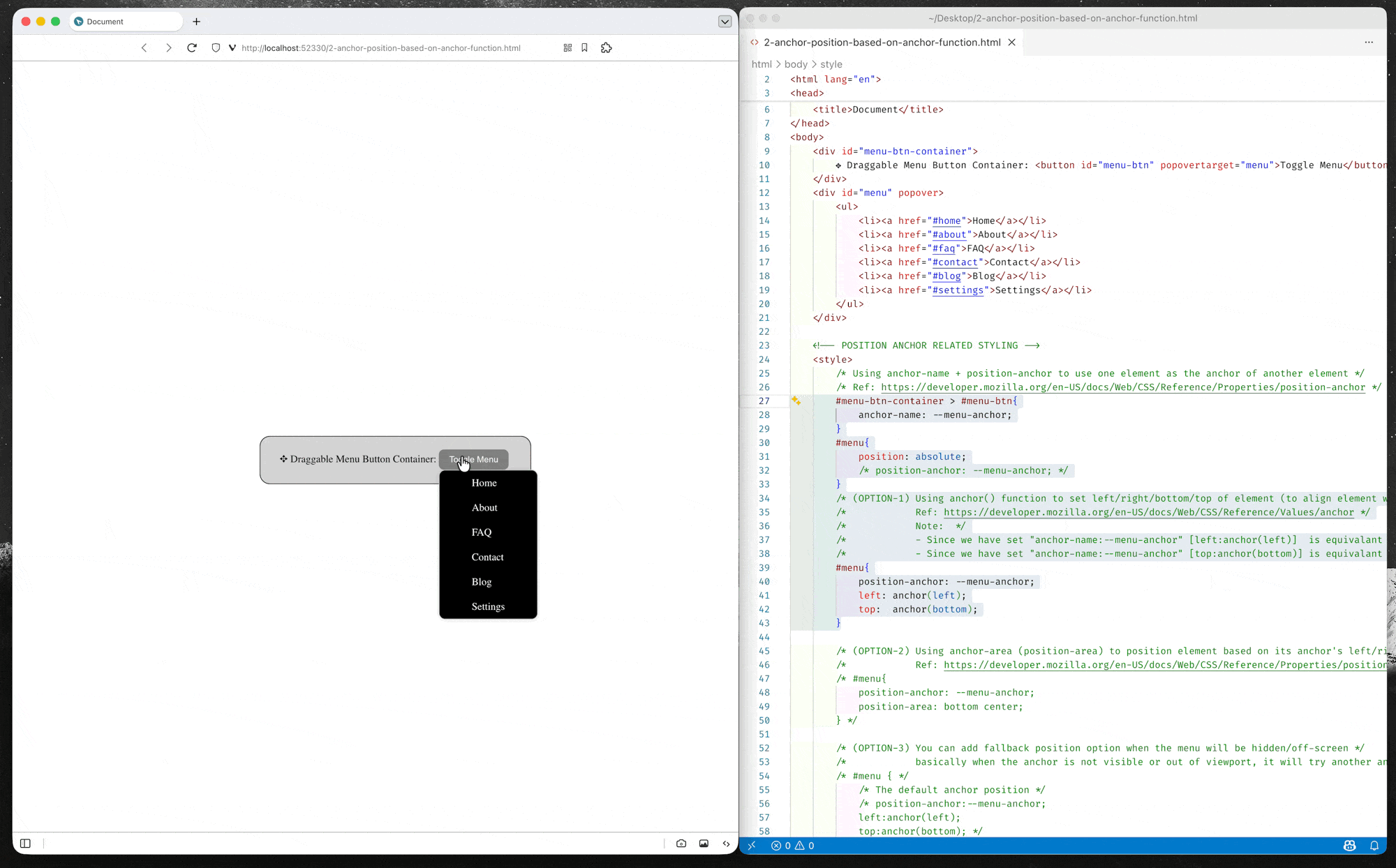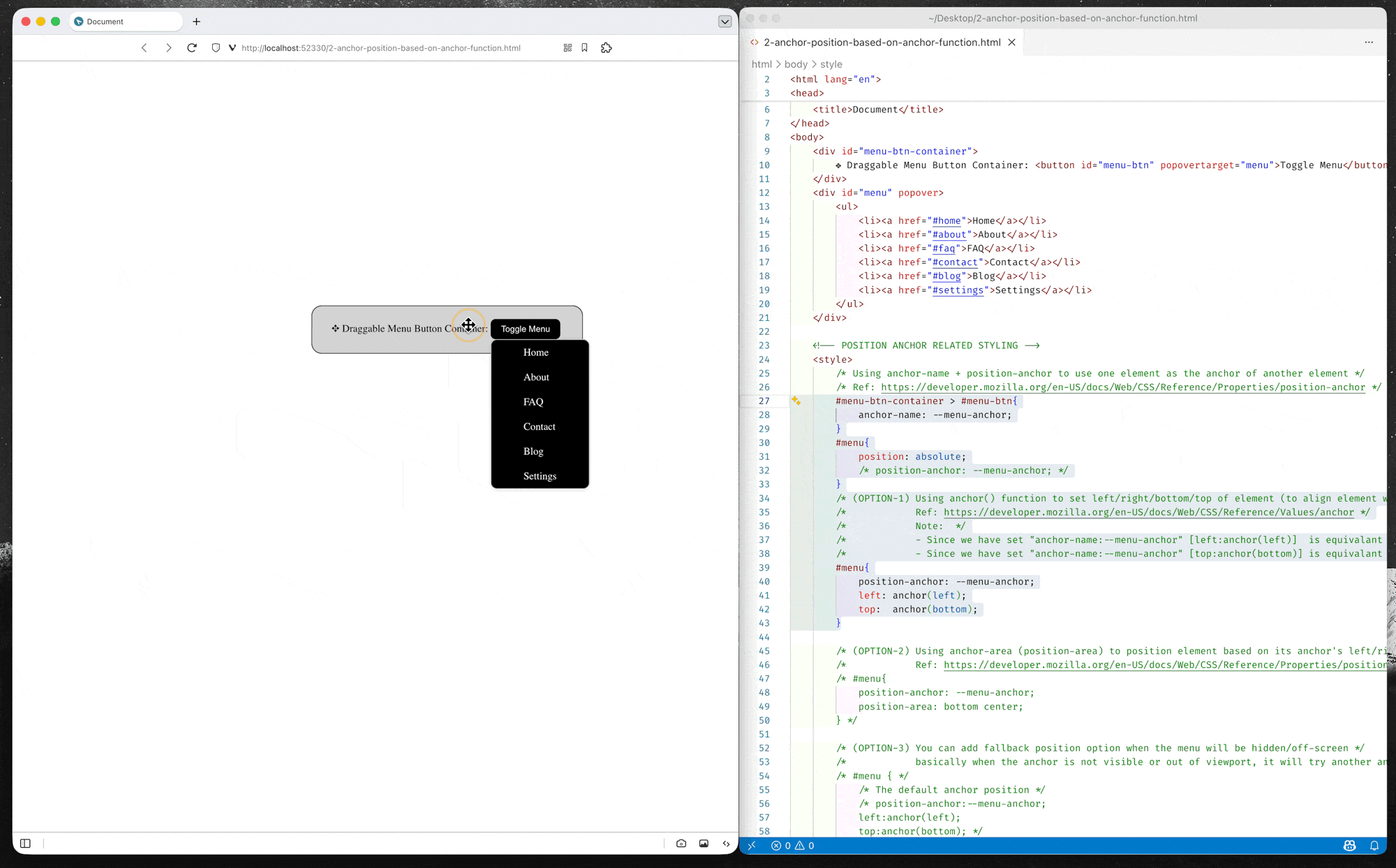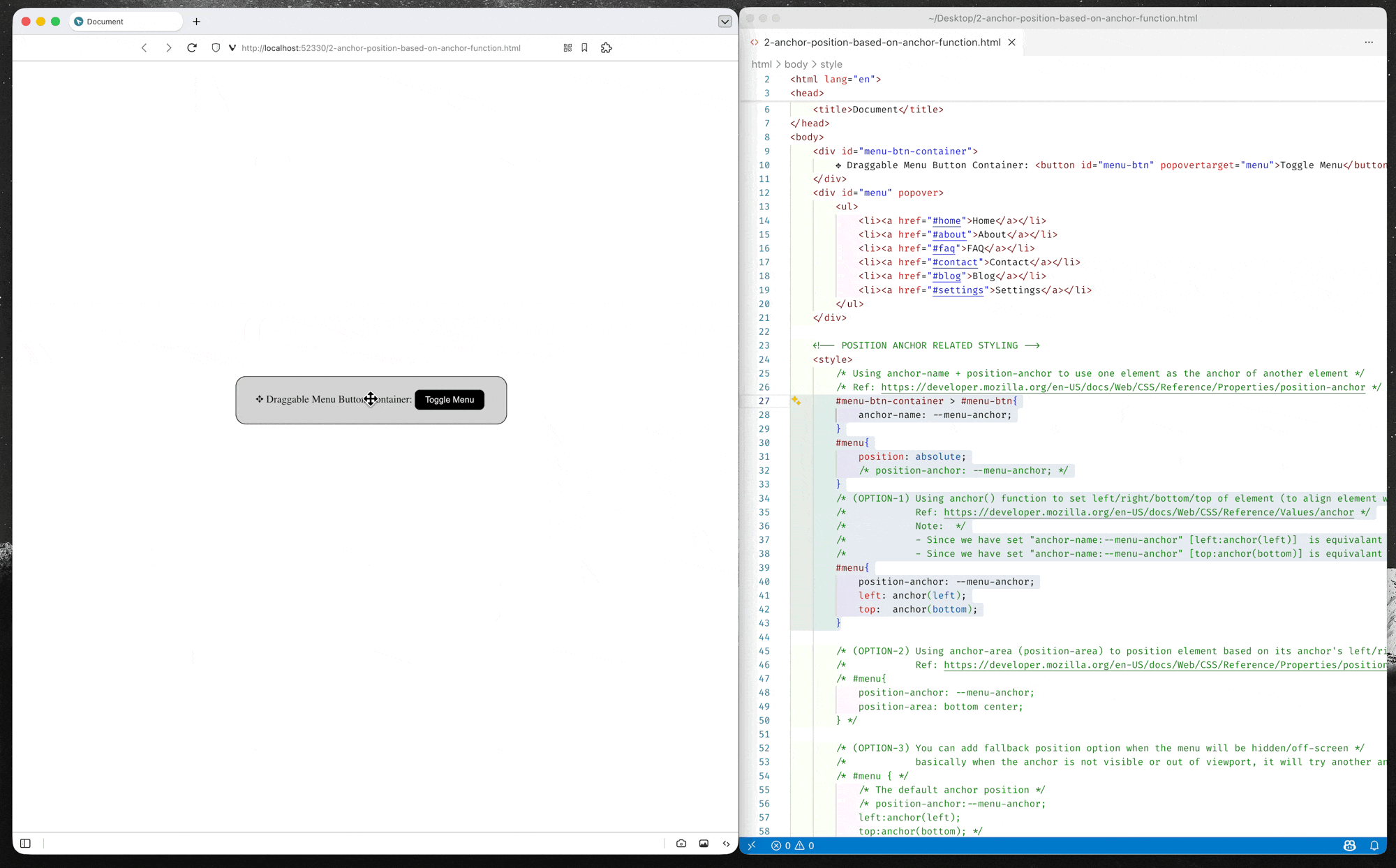
(source code: 2-anchor-position-based-on-anchor-function.html)
Option-2: Position using position-area property
The
position-areaproperty provides an alternative to theanchor()function for positioning elements relative to anchors. Theposition-areaproperty works on the concept of a 3x3 grid of tiles, with the anchor element being the center tile. Theposition-areaproperty can be used to position the anchor positioned element in any of the nine tiles, or have it span across two or three tiles.– MDN Documents: Setting a position-area
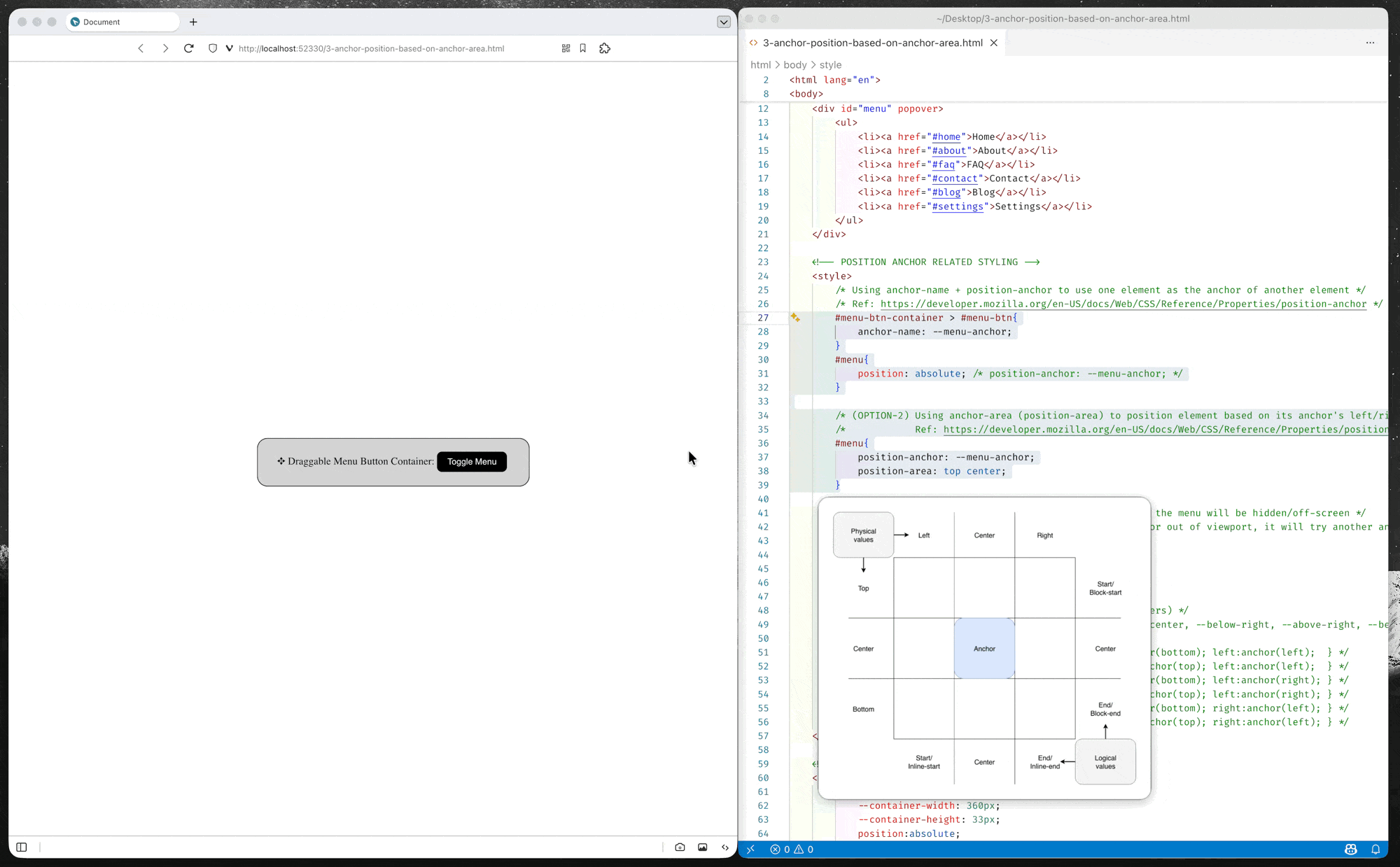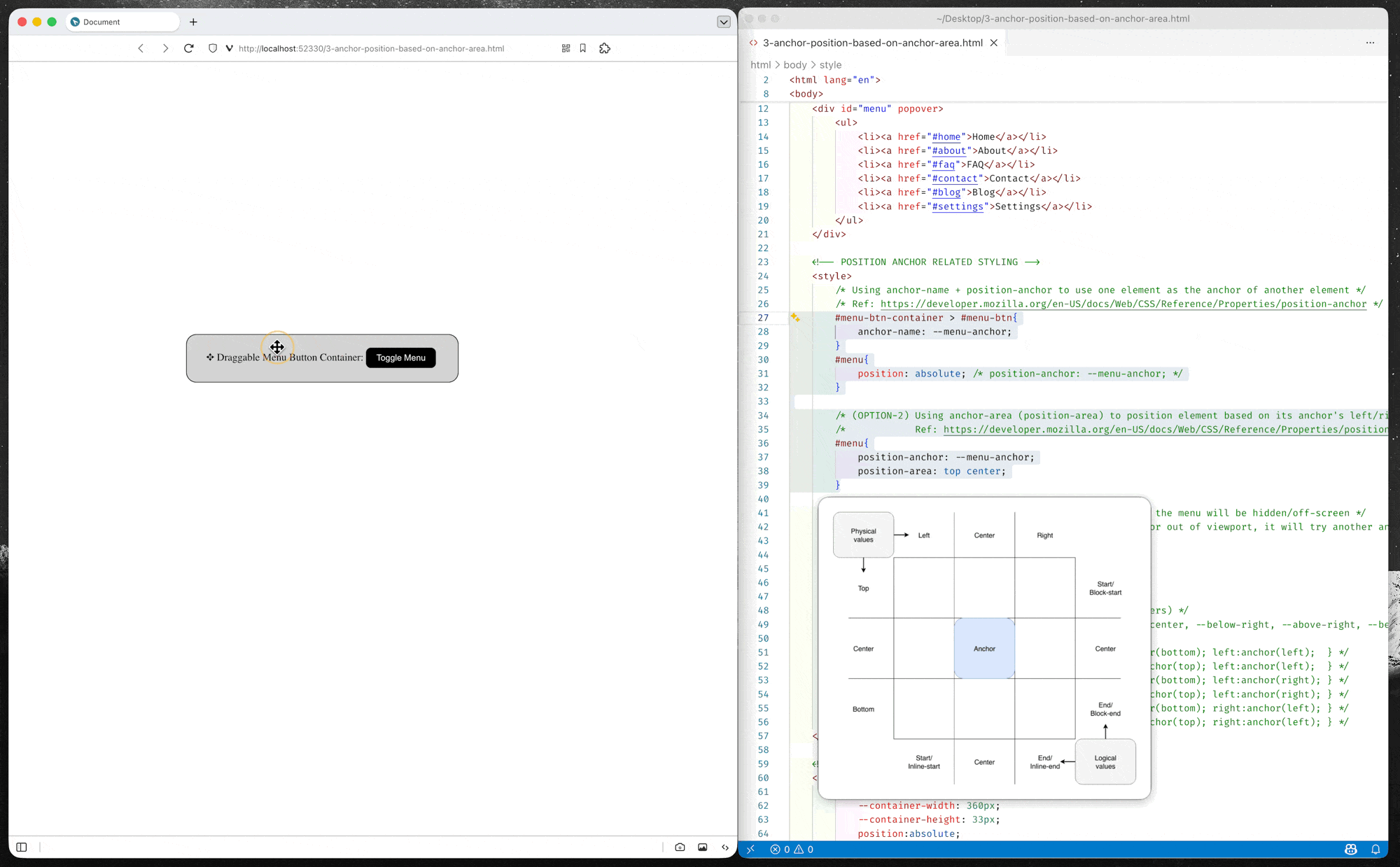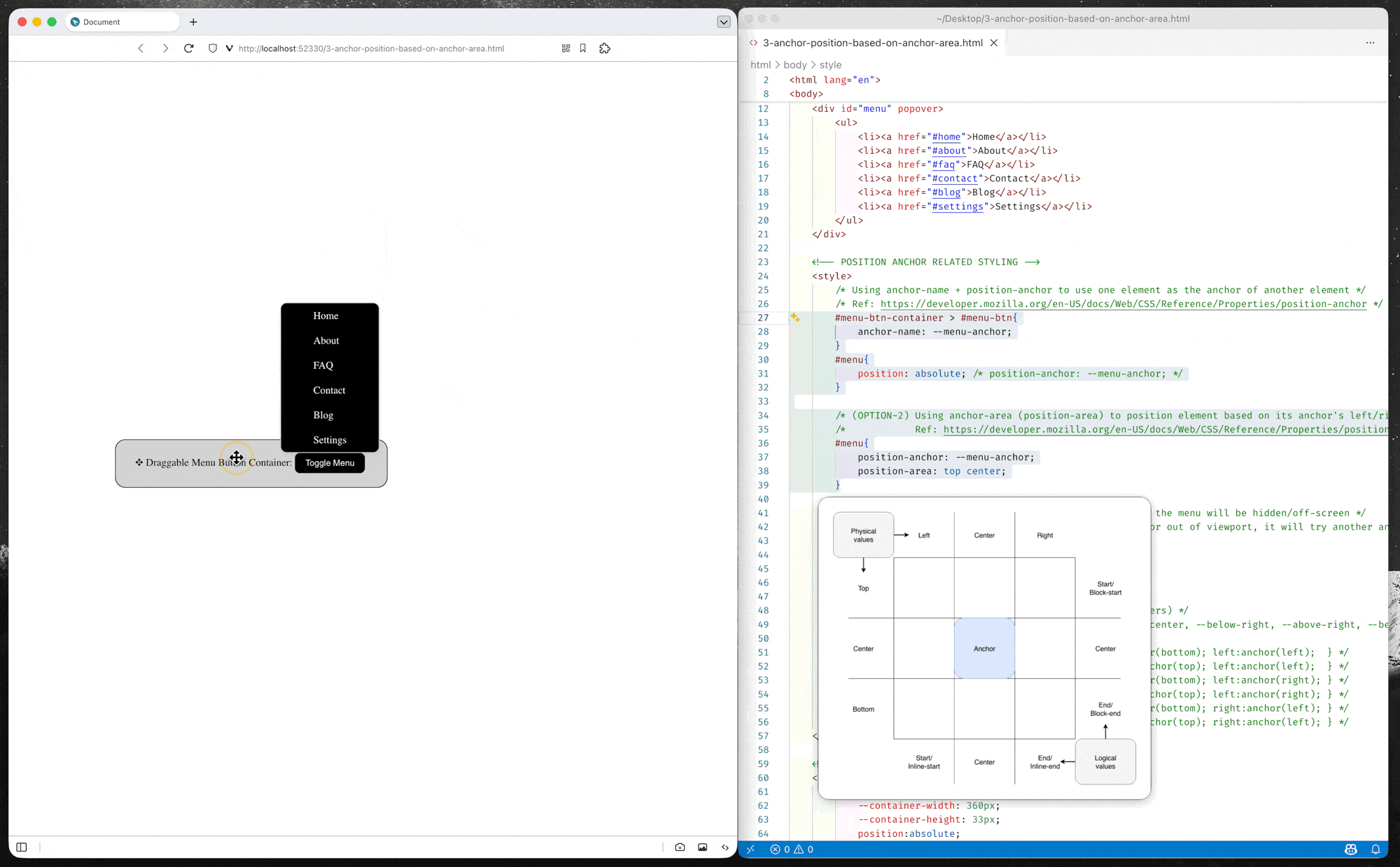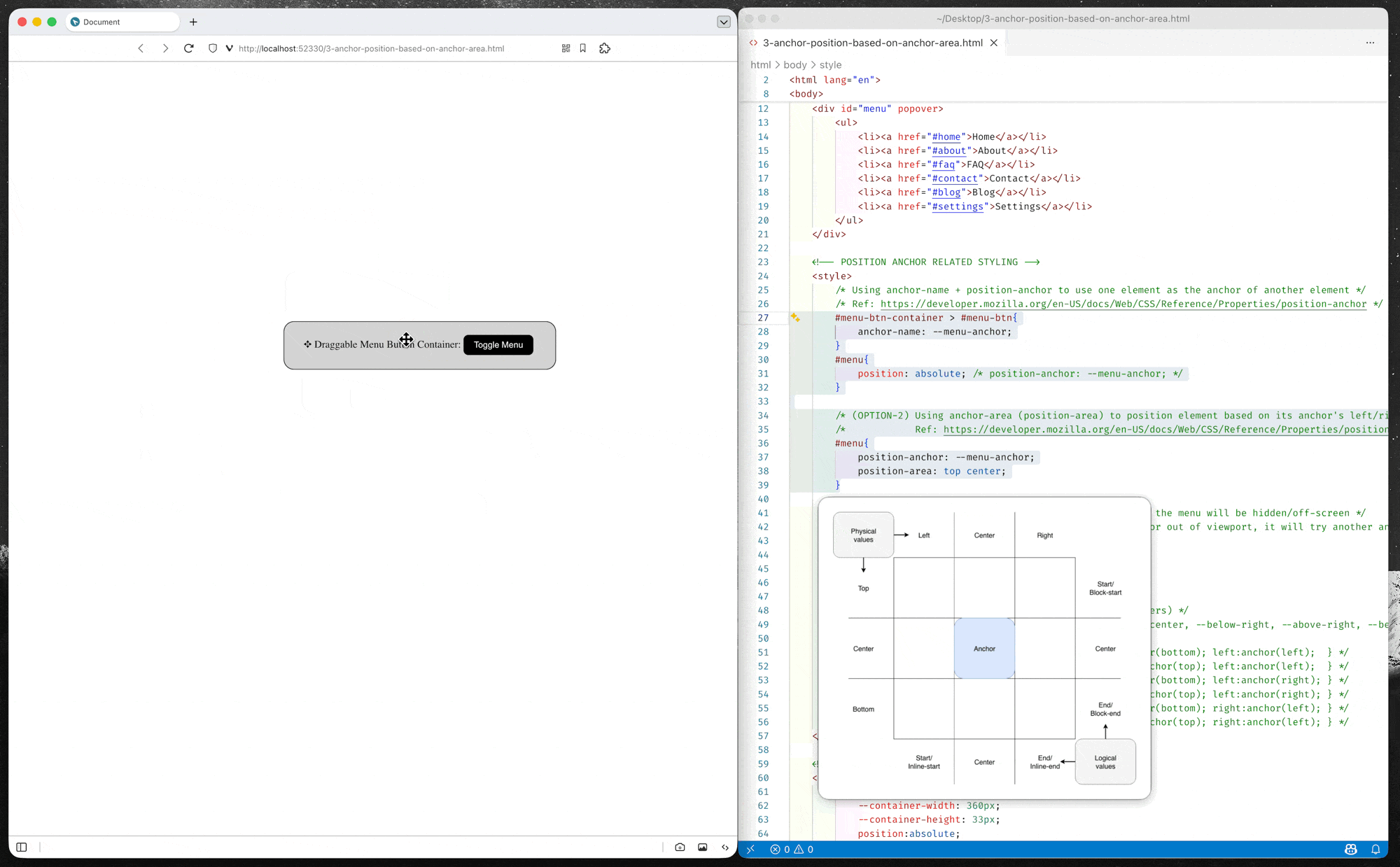
(source code: 3-anchor-position-based-on-anchor-area.html)
Anchor Position Fallback (Alternative Position)
CSS anchor positioning also provides CSS-only mechanisms for specifying multiple alternative positions for an anchor-positioned element. For example, if a tooltip is anchored to a form field but the tooltip would otherwise be rendered offscreen in its default position settings, the browser can try rendering it in a different suggested position so it is placed onscreen, or, alternatively, hide it altogether if desired.
– MDN Documents: Fallback options and conditional hiding for overflow
(*You can either use anchor() function or anchor-area in the fallback position options)
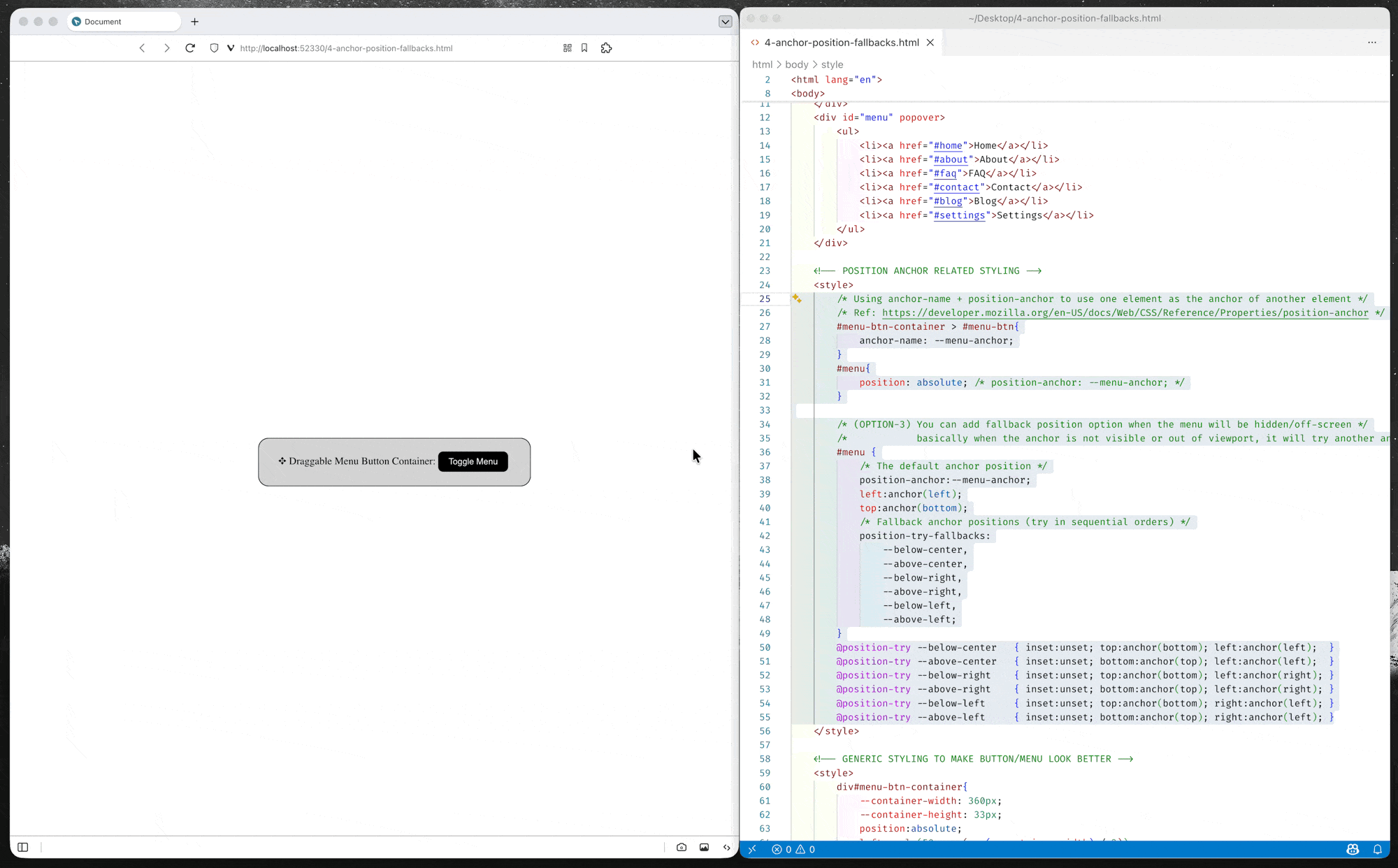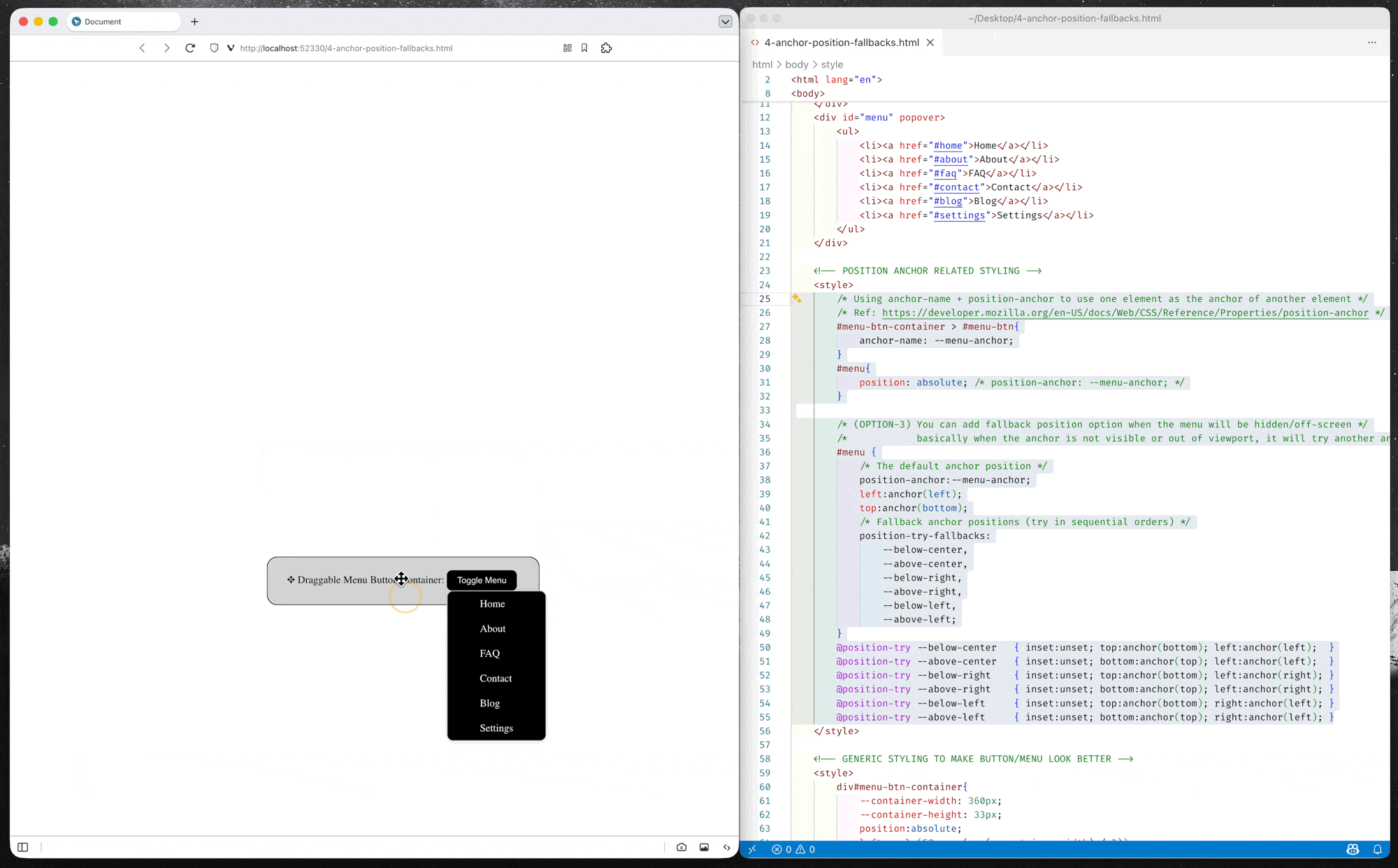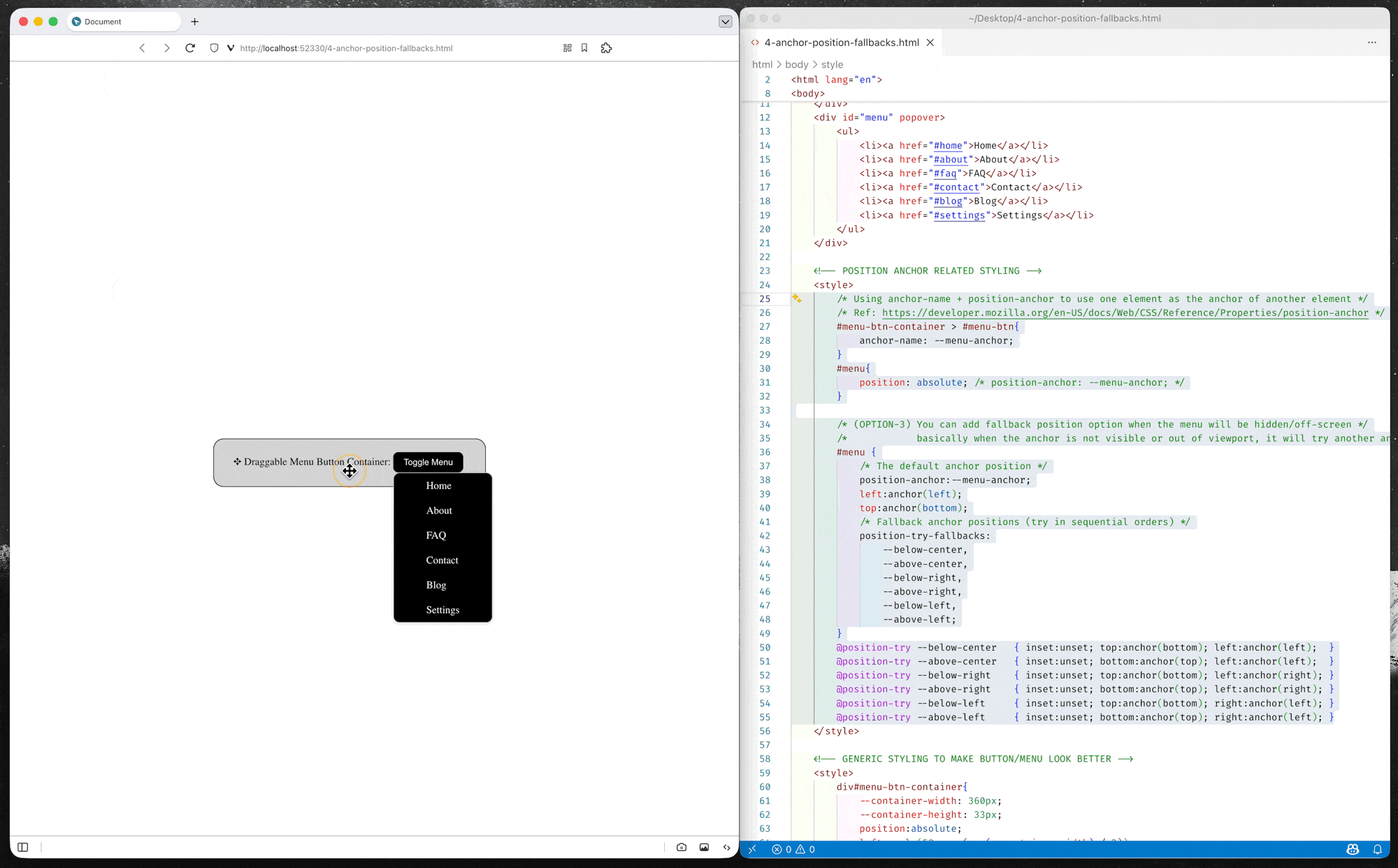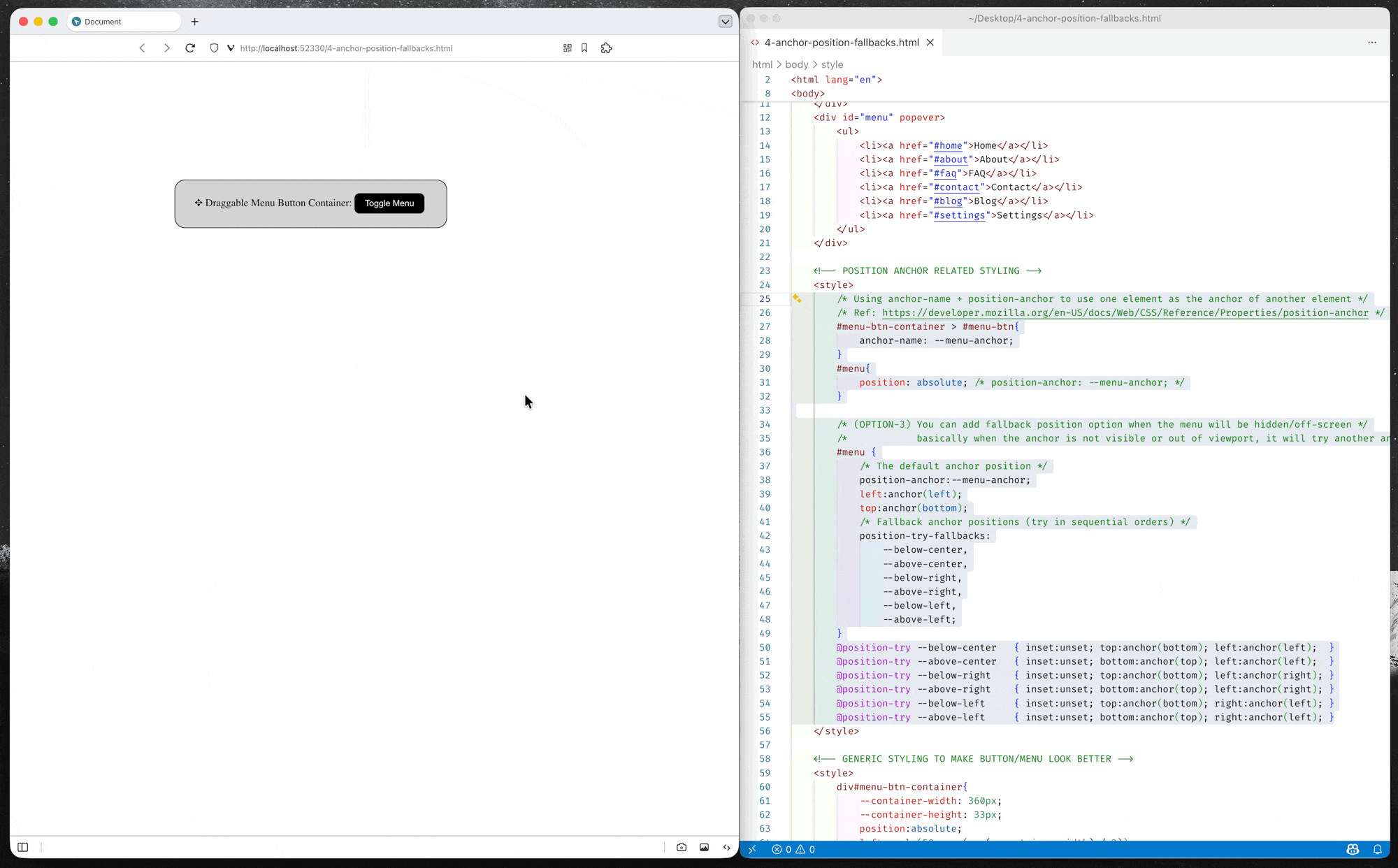
(source code: 4-anchor-position-fallbacks.html)
Reference
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsD9bE_QVAs
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/Guides/Anchor_positioning/Try_options_hiding
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/CSS/Guides/Anchor_positioning/Using
- https://www.w3schools.com/howto/howto_js_draggable.asp (draggable container’s JavaScript)