TLDR;
Use OKLCH over HSL/HSV/RGB/HEX because:
Readable and Predictable: OKLCH is human-readable and offers predictable results for color transformations, unlike RGB or hex.
Perceptual Lightness: OKLCH provides consistent perceived lightness, unlike HSL, which improves color modifications and accessibility.
Palette Generation: Designers can define formulas to automatically generate color palettes, simplifying design systems.
Why is OKLCH better than other colours?
Readable and Predictable (OKLCH vs HEX, RGB, OKLAB)
Compared to other colour options such as RGB and Hexadecimal, OKLCH, HSL (and OKLAB, HSV) is much more readable and predictable by the human brain if you are familiar with the cylindrical colour model, hence making it convenient for colour modification.
You can easily visualise the following cylindrical model in your brain and easily identify which component to change if you want a variant of the existing colour. (for instance, to reduce the lightness of oklch(0.7 0.5 0.0) to 50% of the original, it will be oklch(0.5 * 50% 0.5 0.0))
(Read More on: OKLCH vs. RGB/Hex section of this blog post: OKLCH in CSS: why we moved from RGB and HSL)
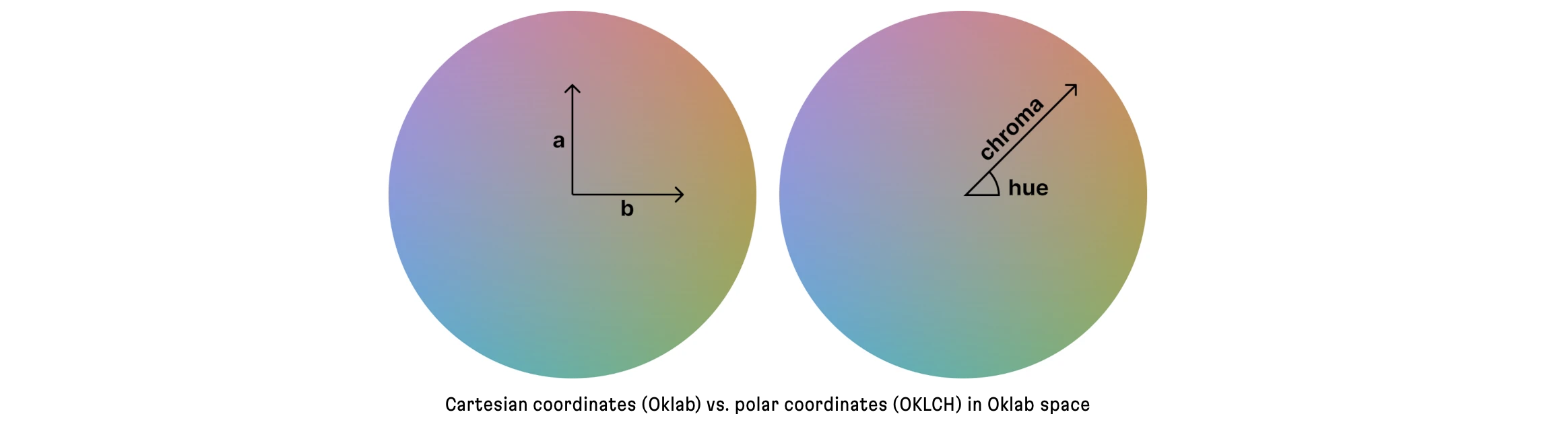
And personally speaking, I much prefer the OKLCH polar coordinate compared to the Cartesian coordinates by OKLAB, but you may have a different preference…
Perceptual Lightness (OKLCH vs HSV, HSL)
Firstly, because perceptually speaking, HSL (HSV) is not visually uniform (deformed color space), if we keep the saturation and lightness/value value fixed and only changing the hue, to the human eye, the different colors from red to blue do not look uniformly distributed!
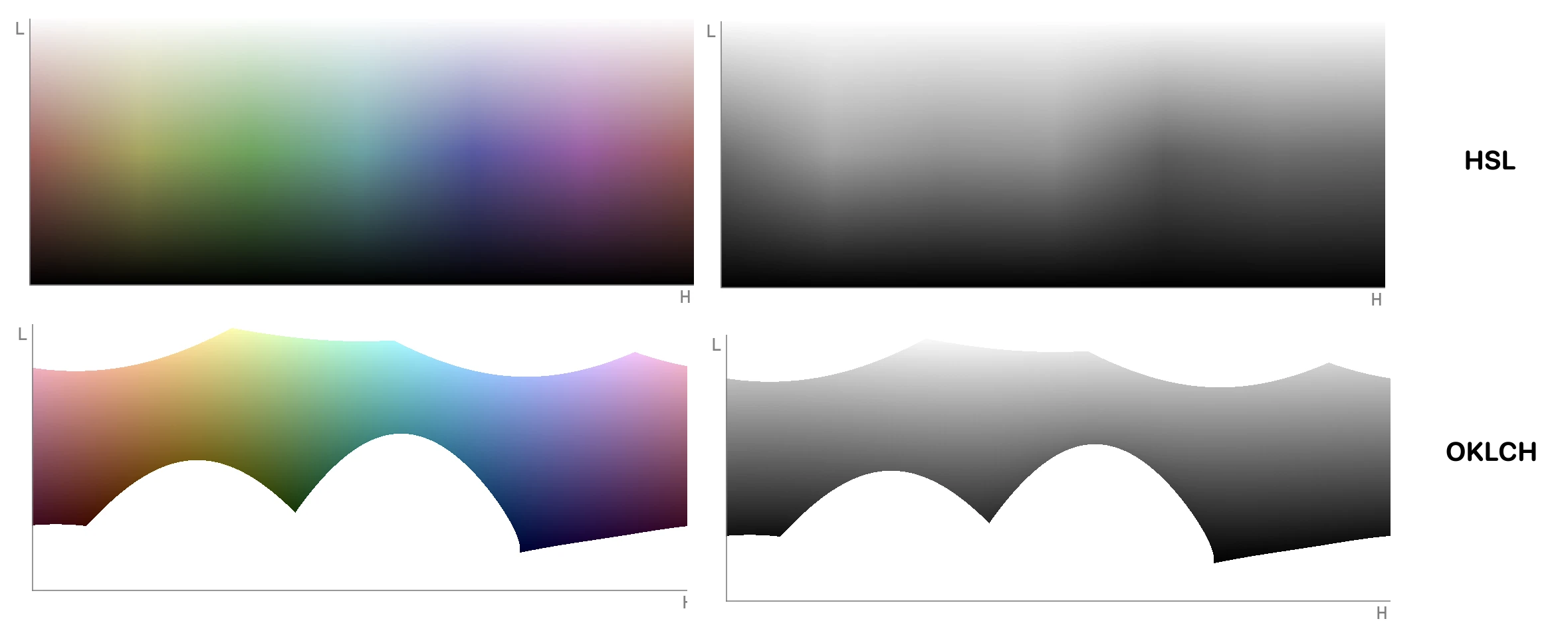
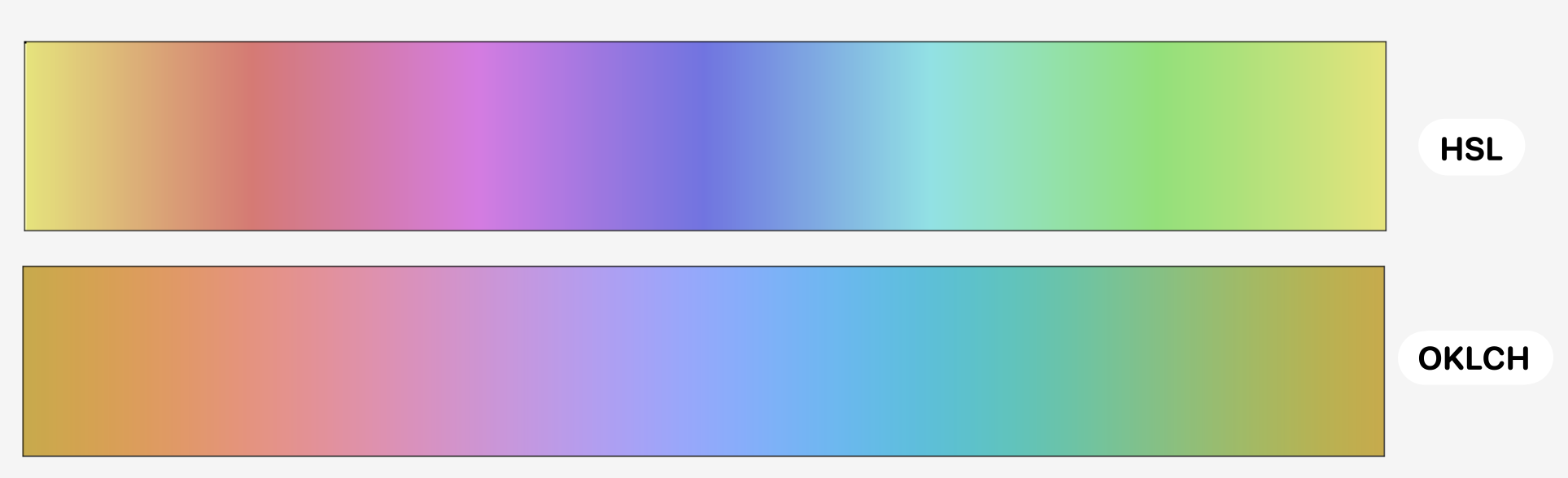
Below is a comparison between HSL and OKLCH (similar outcomes will apply to the comparison between HSL/HSV and OKLAB/OKLCH as well)

The problem of HSL can lead to problems such as shown below: changing only the “HUE” component of the button will lead to a contrast issue because the perceptual lightness of the “green vs purple” of the same lightness and saturation is different in HSV. As a result of the deformed colour space, HSL (HSV) is bad for colour modifications and colour palette generation.
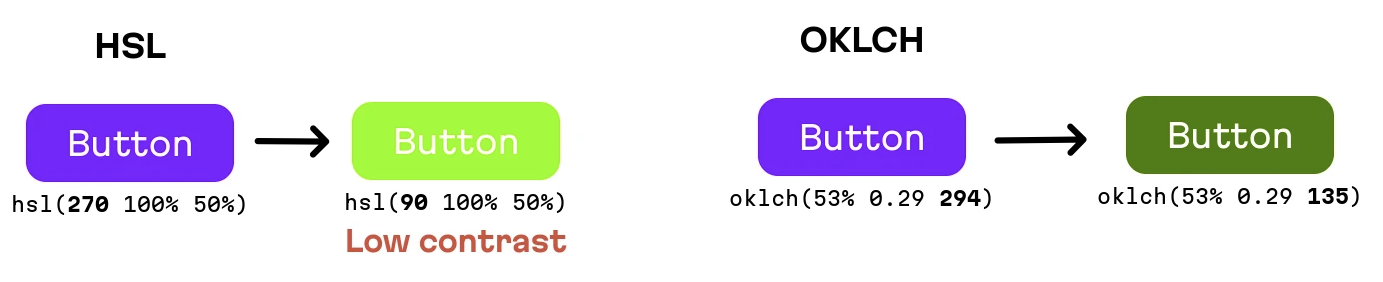
But with perceptual uniformity comes with trade off:
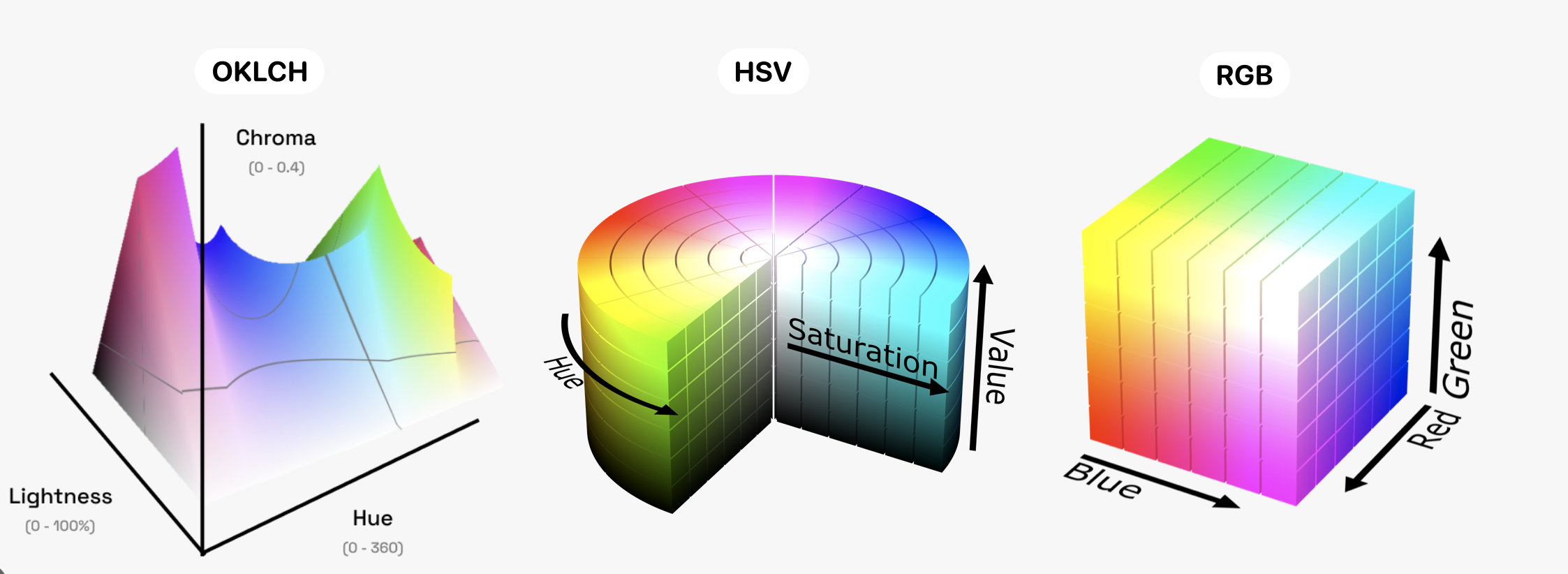
It can be a little tricky to work with OKLch/OKLab though. Because it’s a device independant color space, it can be used to represent any color in CIE XYZ color space. But your display doesn’t support a lot of those colors, so it’s easy to select values that are out of gamut for your display which will be clipped ↓.
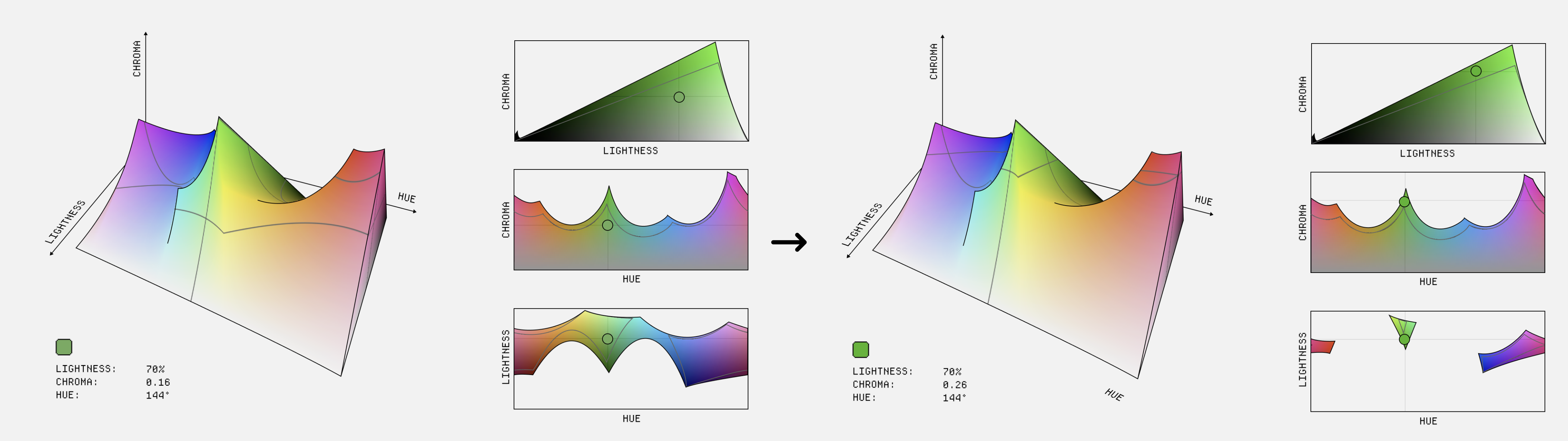
he chroma peaks are also relative to the hue and lightness so you can’t actually be sure that there will be an equivalent chroma in a different hue. You can see this problem with green, which has the highest chroma. Here’s a fairly washed out green where you can see that we can find an equivalent in other hues (left) If we increase the chroma from 0.16 to 0.26, you can see that we have almost no other hues that can match that chroma and lightness combination in the P3 gamut (right)
(If you are interested in the colour science math behind this, you can check out these posts:
- Björn Ottosson: OKLAB
- OKLCH in CSS: why we moved from RGB and HSL
- Pixels And Color: what Is A Color Space
Palette Generation (OKLCH vs HSL, HSV)
With the CSS Color 5, you can take one color and change the individual component of the colour format.
| |
(As previously stated in the “Perceptual Lightness” section, though HSL can also be benefited from this feature, the outcome is less predictable due to its deformed color space, hence many teams have asked the community to avoid HSL for design system palette generation)
You can use the folowing tool to generate/test your color palette:
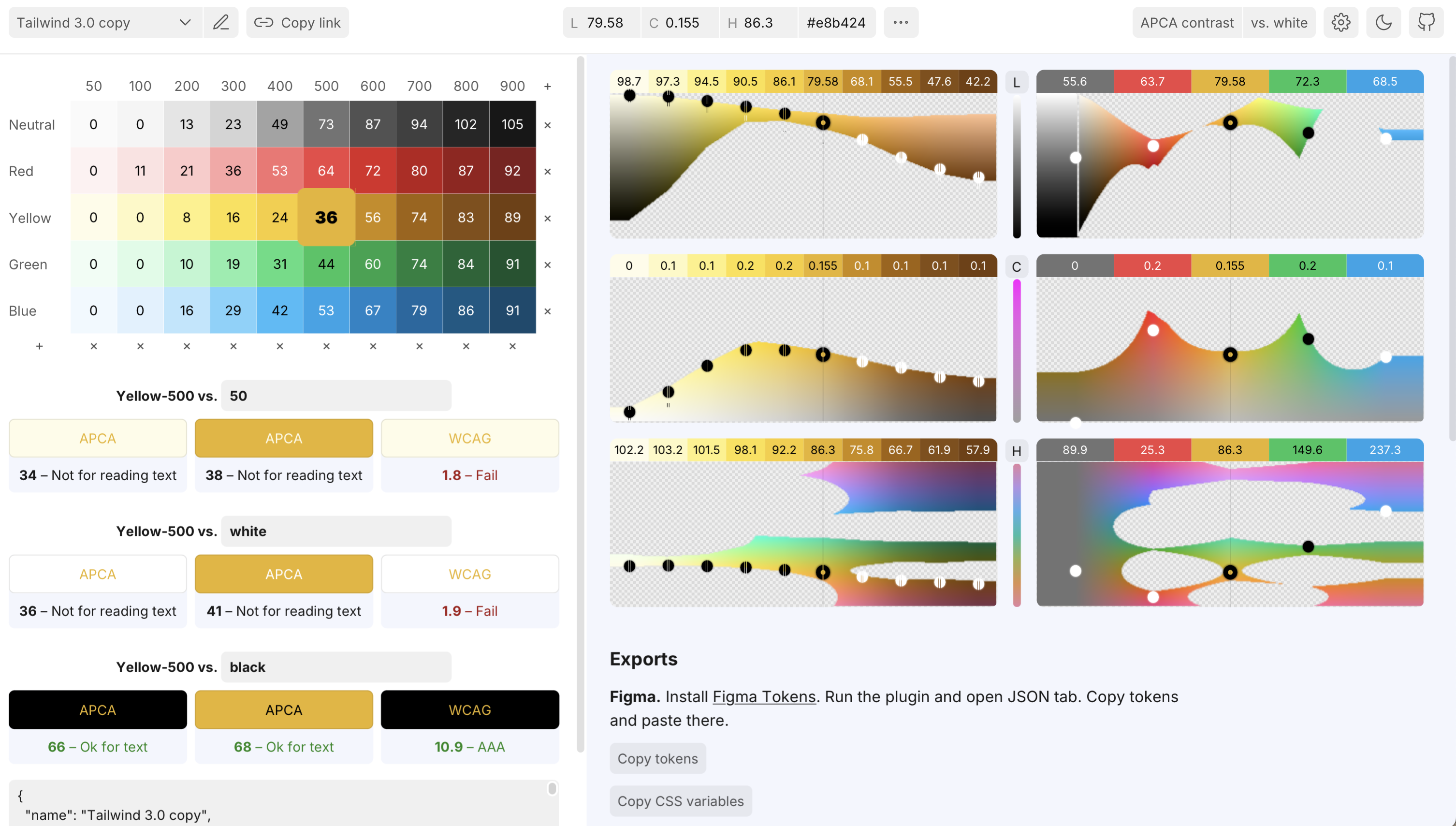
(OKLCH Color Palette Generator / Contrast Testing: https://huetone.ardov.me)
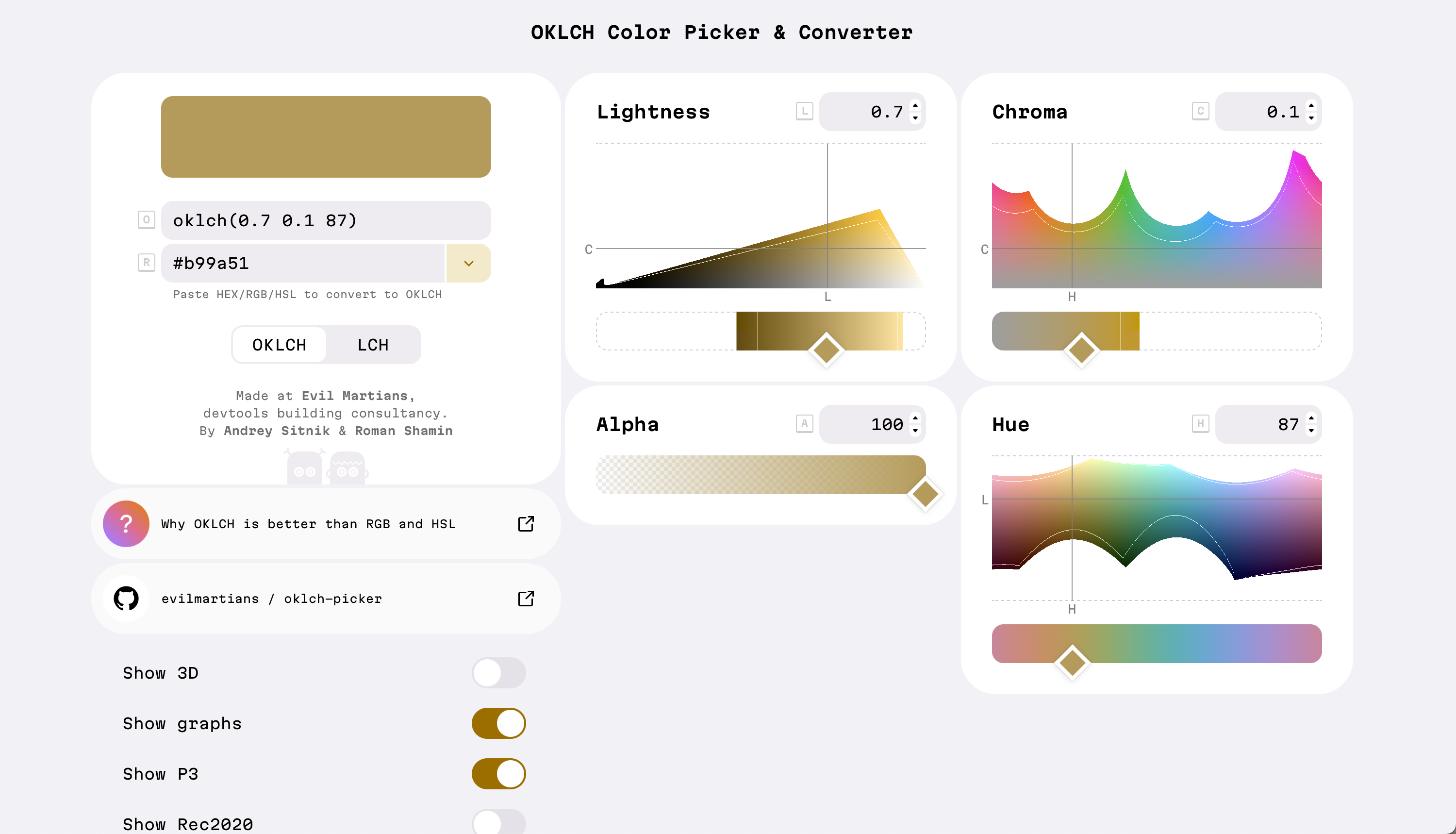
(OKLCH Color Picker & Converter: https://oklch.com)
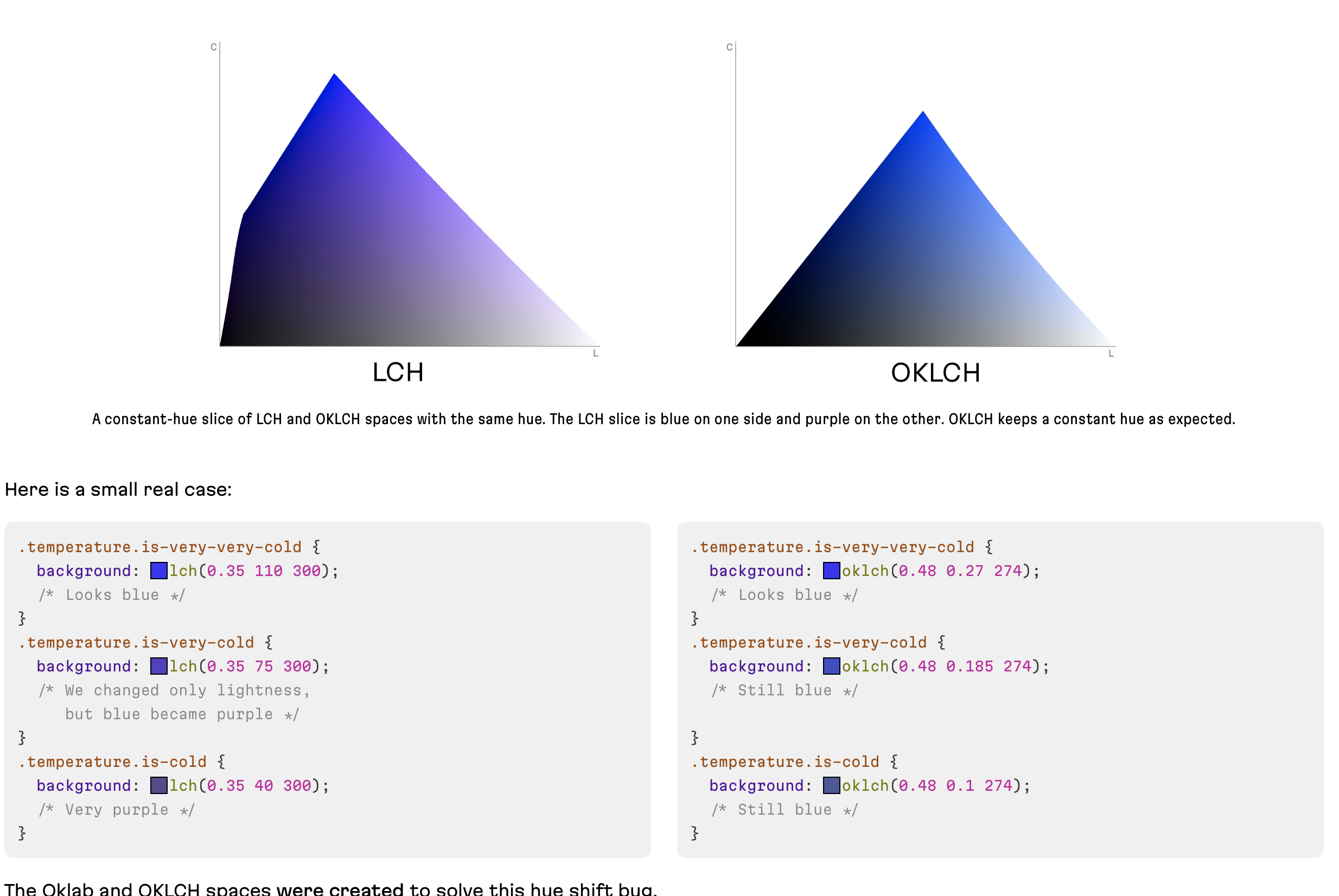
No Unexpected Hue Shift (OKLCH vs LCH)
I’m no color scientist so I’ll use the words from the blog post by Andrey:
LCH is a good format on top of the CIE LAB (Lab) space that was created to solve all the problems of HSL and RGB. It can encode P3 colors and, in most cases, produces predictable color modification results.
But LCH has one painful bug: an unexpected hue shift on chroma and lightness changes in blue colors (between hue values of
270and330).
All Color Options Available
(as of when this post is written)
Here’s a summary of color options available in CSS, including their advantages and the specified color models:
Named Colors:
- Quick and easy (to remember) for basic usage.
Hexadecimal:
Compact representation;
Widely recognized in web design.
RGB:
Direct control over color components;
familiar to many developers.
HSL / HSV:
Intuitive for color manipulation based on human perception.
The difference between HSL and HSV can be found on this image found on Wikipedia: Fig. 1. HSL (a–d) and HSV (e–h).
OKLAB/OKLCH:
- Intuitive for users familiar with cylindrical color spaces, human readable;
- maintains perceptual/visual uniformity
- OKLAB,OKLCH are the perceptually/visually uniform version of LAB,LCH. The difference between LAB and LCH can be found at this image: Color Science Explained: Lab and LCH Color - Kwality Labels Inc)
CSS Color Level 4 (Alpha / Opacity):
- Modern syntax allows for easy handling of transparency, enhancing flexibility in design.
Below are their syntax and examples of usages:
| Color Model | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Named Colors | Just use the color name | red, blue, etc. |
| Hexadecimal | #RRGGBB or #RGB | #ff0000 |
| RGB | rgb(red green blue) where each value is 0–255 | rgb(255 0 0) |
| HSL | hsl(hue saturation lightness); hue in degrees, saturation/lightness in % | hsl(0 100% 50%) |
| HSV | hsv(hue, saturation, value); hue in degrees, saturation/value in % | hsv(0 100% 100%) |
| OKLAB | oklab(L a b); L is lightness, a/b are color axes | oklab(0.5 0.5 0.5) |
| OKLCH | oklch(lightness chroma hue); lightness 0–1, chroma 0–1, hue in degrees | oklch(0.5 0.5 0) |
| Alpha/Opacity | hsl(hue saturation lightness / alpha),oklch(lightness chroma hue / alpha) | hsl(0 100% 50% / 0.5), oklch(0.5 0.5 0.5 / 0.5) |
Reference
Tools
OKLCH Color Palette Generator / Contrast Testing: https://huetone.ardov.me
OKLCH Color Picker & Converter: https://oklch.com (pelase turn on the 3D tool, it is very helpful for understanding !)